DPF / OPF / GPF DELETE (PARTICULATE FILTER)
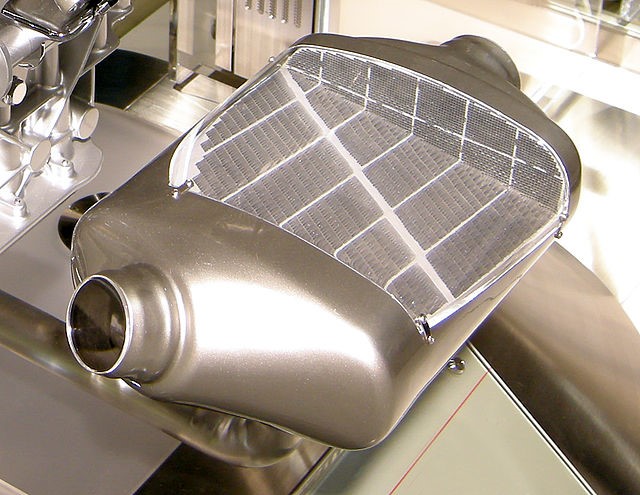

What is DPF (particulate filter)
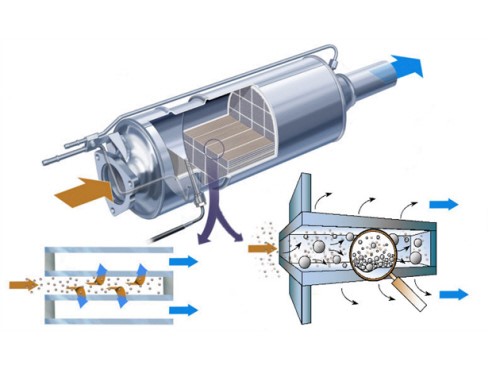
DPF stands for Diesel Particulate Filter. Diesel particulate filters trap and store harmful soot particles, reducing toxic emissions from the exhaust into the air. The particulate filter (DPF) Delete software modification makes sure these soot particles will no longer be stored in the engine.
A particulate filter is usually made of ceramic material. A particulate filter is installed as close as possible to the engine in the exhaust system, where the soot particles collect in the filter. In the particulate filter, the captured soot particles are burned periodically, every 200 to 1000 kilometers. This combustion is referred to as regeneration. This spontaneous combustion requires a temperature of about 600°C, which is only reached at very high engine loads. To achieve regeneration even at lower engine loads, the ECU will artificially increase the temperature of the exhaust gases. Before the car starts the regeneration process of the particulate filter, it must meet many requirements such as correct combustion values, temperature and correct feedback from the sensors.
Also, the filter may be saturated (full) and then can no longer be cleaned. So a lot can go wrong here, and ultimately adversely affect the engine.
Price: from €350,-*
* ex. VAT.
Benefits DPF/OPF Delete
- More power
- Better vehicle acceleration
- Improved throttle response
- Lower exhaust gas temperature
- Lower maintenance and replacement costs
- Longer lifespan
Disadvantages DPF/OPF Delete
- Increased exhaust and particulate emissions
- High probability of failing MOT emissions tests
- Less environmentally friendly